We are leading London specialists in investigating Heart Rhythm Problems
Types of Heart Rhythm Disturbances
There are many types of rhythm disturbances and the terms use to describe these can be confusing. Please use the follow section to find out more out various rhythm problems. Rhythm problems can arise from the atria (collecting chambers) ventricles (pumping chambers) or the junction between them.
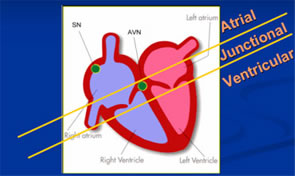
Heart rhythm problems can originate in different parts of the heart.
Supraventricular Tachycardia
This term describes several other types of fast heart rhythms that are typically not dangerous, but can cause symptoms of palpitations, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
They can start suddenly and stop suddenly, and may last for minutes or hours, with a rapid but steady pulse during the episode. The fast rhythm is usually caused by either an irritable spot that fires rapidly (atrial tachycardia, or AT), or by an electrical “short circuit” that involves an extra electrical connection between the top and bottom chambers of the heart (atrioventricular node re-entry or AVNRT; atrioventricular reentry with an accessory pathway or AVRT). Treatment options include medications or a catheter ablation procedure.
Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is similar to AF, characterized by a rapid heartbeat.
Instead of rapid disorganized signals in the atria, however, AFL is caused by a single electrical wave that circulates very rapidly in the atrium (usually the right atrium), about 300 times a minute, leading to a very fast, steady heartbeat. Treatment can be with medication, but radiofrequency ablation, and invasive treatment is usually curative.
Sick Sinus Syndrome
Also called “sinus node dysfunction,” SSS is not a specific disease, but a group of signs or symptoms that indicate the heart’s natural electrical pacemaker, the sinoatrial node, is not functioning properly.
In SSS, the heart rate may be abnormally slow at rest (bradycardia), or it may fail to speed up with activity or in response to your own adrenaline (chronotropic incompetence). However, at other times, it can run fast. If symptoms develop from SSS, or if the heartbeat is extremely slow even without symptoms, a permanent pacemaker is the primary treatment.
Sinus Tachycardia
A harmless rhythm, sinus tachycardia is a normal increase in heart rate that happens with fever, excitement and exercise.
It rarely requires treatment aside from treating the underlying problem, such as anemia, infection, or hyperthyroidism. Rarely, the sinus node can cause the heart to beat faster than it should without any underlying cause. If symptoms result, the condition is known as “inappropriate sinus tachycardia,” and some treatment options are available.
Ventricular Tachycardia
Characterised by a very fast heart rate, VT usually is seen in the setting of other serious heart disease, and may be life-threatening.
Occasionally, it occurs in people with normal hearts. If it does not stop on its own, VT usually requires prompt treatment with either medication or an electrical jolt to the heart (electrical cardioversion). Further treatment of VT may involve antiarrhythmic medications, a catheter ablation procedure, or rarely surgery. Often, people with VT and heart disease are protected by implantation of a defibrillator (ICD). Because VT may lead to ventricular fibrillation (VF), it is considered a serious condition that warrants aggressive monitoring and treatment.
Ventricular Fibrillation
Sudden cardiac death (SCD), caused by ventricular fibrillation, poses the greatest threat of all arrhythmias, and accounts for half of all cardiac deaths. In VF, the heartbeat is rapid and chaotic, which prevents the lower heart chambers, or ventricles, from pumping blood to the brain or body.
During VF, the blood pressure falls to zero, and the person falls unconscious in seconds. The lack of blood and oxygen throughout the body, and especially to the brain, is deadly within a few minutes if not treated promptly with defibrillation (shock).
Sometimes, VF can happen during a heart attack (myocardial infarction), because the heart muscle is irritated by the sudden blockage of an artery. VF can also happen at other times, and be caused by previous heart damage or an inherited (genetic) heart condition. It is important to realize that VF is an electrical disorder of the heart (not the same thing as a “heart attack”) and may or may not be related to a problem with clogged arteries that supply the heart with blood.
Premature contractions
Extra, early, or “skipped” beats are the most frequent cause of irregular heart rhythms.
These early, extra beats are weak and may not be felt in the chest or in the pulse at the wrist, which is why symptoms are frequently described as “skipped” beats. Extra beats can come from either the upper chambers (premature atrial complexes, PACs), or the lower chambers (premature ventricular complexes, PVCs) of the heart.
Long QT syndrome
Long QT Syndrome is a disorder of the electrical system in which the heart cells take longer than normal to recover electrically after each heartbeat.
It can be inherited, acquired after taking certain medications, or caused by a combination of heredity and medications. People with LQTS may be susceptible to ventricular fibrillation, which can lead to death. They may need specialist care and an implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD).



