Carotid artery stenosis occurs when the carotid arteries, which carry blood to the front part of the brain, become narrow. This narrowing occurs due to the buildup of fatty deposits, much like in the coronary arteries, which cause heart attacks if not treated. The hardening of these arteries, known as artery stenosis, reduces blood flow to critical brain areas. If a piece of plaque breaks off, it can travel to the brain, leading to a stroke.
Carotid Artery Stenosis and Stroke
Strong evidence suggests a clear connection between carotid artery disease and stroke. If you have a history of stroke and a narrowing is detected in your carotid arteries, urgent treatment may be necessary.
For individuals who have not suffered a stroke but are experiencing symptoms of carotid artery blockage, such as:
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Mini – strokes or minor strokes (TIAs)
In this case, treatment may still be required. Your specialist will carefully discuss the potential risk factors and benefits of continuing medication, opting for surgery, or having a stent.
Treatment may still be needed if you have no symptoms but a tight narrowing.
Diagnosing Carotid Artery Stenosis
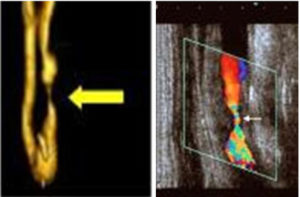
Accurate diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis typically involves a carotid artery scan, often performed using MRI or ultrasound imaging test. After physical exams and carotid bruit checks, these scans help to determine the degree of narrowing in the arteries and guide decisions on the appropriate treatment approach. A CT scan will probably also be done to confirm the narrowing.
Below, you can see detailed images of a private MRI and Ultrasound with a carotid narrowing:
Carotid Artery Blockage Treatment Options
The primary treatment for carotid artery blockage is carotid endarterectomy, a surgery that removes fatty substances from the blood supply and improves blood flow to the brain.
However, there are other treatment options that your doctor may discuss, including:
- Private Carotid Artery Stenting: A less invasive surgical treatment option, often tested in clinical trials, where a stent is placed to keep the blood vessel open.
- Medication for Heart and Stroke Conditions: Medical treatment often manages symptoms and reduces artery stenosis progression.
- Lifestyle Changes: To manage your vascular health, adopt a healthy diet, quit smoking, and increase physical activity.
If you’re experiencing carotid artery blockage symptoms, contact our office to schedule an appointment. Early diagnosis and treatment, such as carotid endarterectomy, can reduce the risk of stroke and blood clots and improve long-term outcomes.
Article by Dr Malik, a leading UK cardiologist. He works at One Welbeck Heart Health – London’s Largest Private Cardiology Group, and at Hammersmith Hospital, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, one of the largest NHS Trusts in the UK.