Fainting is uncommon after early childhood but can still occur in some individuals, especially in stressful or hot conditions. There are various causes, ranging from simple issues like sudden drops in blood pressure when standing up to more severe conditions such as heart valve narrowing and significant heart rhythm problems. Sometimes, the cause is unrelated to the heart, and further evaluation by a neurologist may be necessary to rule out conditions like epilepsy.
Blackout Symptoms and Fainting Symptoms
Blackout symptoms and fainting symptoms share many similarities, which may vary in severity and duration:
- Dizziness: A sensation of spinning or losing balance.
- Lightheadedness: Feeling faint or about to pass out, often occurring when standing up quickly.
- Blurred Vision: Visual disturbances like darkening or tunnel vision often precede fainting.
- Nausea: Feeling sick to your stomach can occur before or after fainting.
- Loss of Consciousness: Brief episodes where the individual loses awareness and collapses.
- Palpitations: Rapid or irregular heartbeats that may accompany fainting episodes.
These symptoms can arise from various causes, including heart conditions, nervous system disorders, or external factors like dehydration or medication side effects.
Blacking out Causes and Fainting Causes
Understanding the causes of fainting symptoms and blackouts is important for proper diagnosis and treatment. Below are some of the most common causes:
- Cardiac Causes: Conditions like aortic stenosis and rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias) can limit blood flow to the brain, triggering fainting.
- Neurological Causes: Conditions like epilepsy or other nervous system disorders may cause fainting.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can reduce blood pressure, leading to fainting.
- Medications: Some drugs, particularly those affecting blood pressure or heart rate, can cause dizziness or fainting as a side effect.
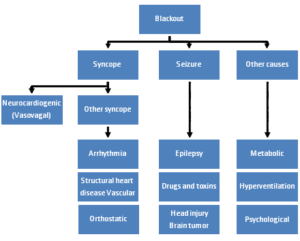
Below is the diagram illustrating possible blackout causes:
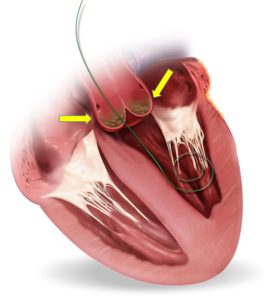
Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis is the narrowing of the aortic valve, restricting blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body.
This condition can be associated with a distinctive aortic stenosis murmur and may lead to aortic stenosis symptoms such as:
- Chest Pain: Often described as a tight, squeezing sensation.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during exertion.
- Palpitations: Rapid or irregular heartbeats.
- Fainting: Sudden loss of consciousness, often triggered by exertion.
Aortic Stenosis causes include:
- Calcium Buildup: Over time, calcium can accumulate on the aortic valve, causing it to stiffen and narrow.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Some people are born with a narrower aortic valve.
- Rheumatic Fever: A complication of untreated “strep throat” that can damage the aortic valve.
Vasovagal Syncope
Vasovagal syncope (pronounced sin-cope-pee) is a common type of fainting caused by a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure.
Symptoms of Vasovagal Syncope:
- Dizziness and Nausea: Often occur before fainting.
- Cold Sweat: Sweating excessively before losing consciousness.
- Visual Disturbances: Blurred or tunnel vision may precede fainting.
Vasovagal Syncope is often caused by:
- Emotional Stress: Vasovagal syncope and anxiety, fear, or pain can come hand in hand as it triggers an overreaction of the vagus nerve.
- Prolonged Standing: Standing for long periods can cause blood to pool in the legs, reducing blood flow to the brain.
- Heat Exposure: High temperatures can cause blood vessels to dilate, lowering blood pressure.
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) UK
POTS is a condition that causes the heart rate to increase abnormally when standing up, leading to fainting and other symptoms. It’s commonly caused by autonomic nervous system dysfunction. The body’s automatic control of heart rate and blood pressure is disrupted.
Some of the POTS symptoms are:
- Rapid Heart Rate: A significant increase in heart rate upon standing.
- Dizziness and Fatigue: Persistent feelings of lightheadedness and extreme tiredness.
- Fainting: Sudden episodes of fainting, often triggered by standing for extended periods.
Causes of POTS include:
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic predispositions may increase the likelihood of developing POTS.
- Viral Infections: Infections can affect the nervous system, potentially triggering POTS.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Some autoimmune disorders may damage the nervous system, contributing to POTS development.
- Nerve Damage: Damage to nerves can weaken blood vessels, particularly in the legs and abdomen.
- Low Blood Volume: Reduced blood volume can lead to symptoms similar to those caused by other factors.
Diagnosis of Blackouts and Fainting Causes
Diagnosing the cause of blackouts and fainting is essential for effective treatment. The diagnostic process generally involves:
- Patient History: Gathering information on symptoms, frequency of episodes, and any triggering factors.
- Physical Examination: Checking vital signs, heart rate, and blood pressure.
- Symptom Tracking: Using diaries or monitoring devices to track episodes and related symptoms.
Aortic Stenosis Investigation
If aortic stenosis is suspected, the following investigations may be required:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the heart’s electrical activity to identify abnormalities.
- Echocardiography: Uses ultrasound to evaluate valve function and detect narrowing.
- Blood Tests: Help to identify any related conditions or complications.
- CT Scanning: Provides detailed images of the heart and surrounding structures.
- Coronary Angiography: Typically not needed unless there are concerns about coronary artery disease.
- Lung Function Tests: Assess how well your lungs work, which can be relevant in certain cases.
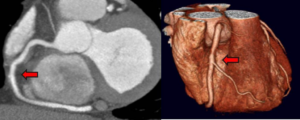
Below is an example of a CT coronary angiogram of the Right Coronary Artery:
Vasovagal Syncope Investigation
To diagnose vasovagal syncope, your doctor will first review your clinical history, which might strongly suggest this condition. If needed, additional tests can be performed to rule out other causes of loss of consciousness. These may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Monitors the heart’s electrical activity.
- 24-Hour ECG Recording (Holter Monitor): Tracks heart rhythm over an extended period.
- Exercise Testing: Evaluates the heart’s response to physical activity.
- Echocardiogram: Assesses the heart’s structure and pump function.
You might also be referred to a specialist unit, such as the Imperial Syncope Diagnostic Unit at Hammersmith Hospital, for a tilt table test. This test involves lying flat on a tilting table, then gradually tilting to a 60-degree angle to simulate conditions that could provoke a fainting episode. Blood pressure and heart rate are monitored during the test to observe any changes associated with symptoms.
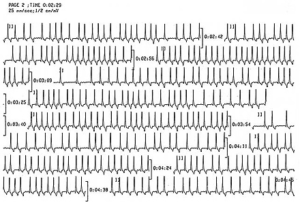
Below is an example of irregular beats seen on a Holter monitor:
POTS Diagnosis in the UK
A diagnosis of POTS can often be suspected based on clinical history and examination. If there is a significant rise in heart rate—more than 30 beats per minute or exceeding 120 bpm—within 10 minutes of standing up from a seated or lying position, accompanied by typical symptoms, POTS may be indicated.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following tests may be conducted:
- Tilt Table Test: Assesses heart rate and blood pressure responses to changes in posture, which helps confirm POTS.
- Blood Volume Testing: Checks for abnormalities in blood volume regulation.
- Autonomic Testing: Evaluates the function of the autonomic nervous system.
Blackouts and Fainting Treatment
Treating blackouts and fainting depends on the underlying cause
Management of Aortic Stenosis
There is no medical therapy (medication) available to treat aortic stenosis, so valve replacement is the primary option. Aortic Stenosis treatment typically involves:
- Private TAVI Surgery: A less invasive procedure that can replace the aortic valve without open-heart surgery.
- Private Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement (SAVR): A surgical procedure to replace the damaged valve with a new one.
If you are diagnosed with aortic stenosis, regular assessments will be conducted to evaluate the severity of the disease and monitor for any worsening symptoms.
Below, you can see the yellow arrows showing the diseased aortic valve and the Edwards Sapien Valve (one of the TAVI valves):
Vasovagal Syncope Treatment
Typically, the following simple vasovagal syncope management strategies help prevent or minimise the episodes:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids, at least 3 litres a day, to stay well-hydrated.
- Recognising Warning Symptoms: Pay attention to signs such as dizziness and nausea. Act promptly by sitting or lying down to prevent syncope.
- Physical Counterpressure Techniques: Perform isometric exercises like clenching your teeth and buttocks and tensing your leg muscles (including quadriceps and calves). This helps “squeeze” blood pooling in the legs back up to the heart and brain.
- Increased Salt Intake: Consider adding more salt to your diet, but only if your blood pressure is normal and you are under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) Treatment
At London Cardiovascular Clinic, POTS specialists will tailor a POTS treatment programme specifically for each patient, which may include:
- Fluid and Salt Intake: Increasing fluid and salt intake can help improve blood circulation and alleviate symptoms. Salt tablets may be occasionally prescribed as needed.
- Medications: Besides standard treatments, drugs such as fludrocortisone, midodrine, or ivabradine may be used to manage symptoms and control heart rate.
- Exercise Programmes: Exercise rehabilitation is crucial to managing POTS. Your specialist will emphasise gradual reconditioning exercises to enhance cardiovascular fitness and overall health.
Ready to Book Your Consultation?
Whether you suspect you may have palpitations or have an atrial fibrillation diagnosis but need expert advice, book your consultation with Dr Malik today. He’ll be more than happy to see you.
Why Choose Dr. Iqbal Malik at London Cardiovascular Clinic?
- Experience: Dr. Malik is a highly experienced cardiologist who offers expert care in diagnosing blackouts and fainting causes.
- Personalised Care: Every patient gets individual attention with clear advice on managing their condition.
- Advanced Testing: Dr. Malik uses the latest technology to accurately diagnose palpitations and atrial fibrillation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does Blackouts and Fainting Investigation Cost?
Insurance
Most private medical insurance policies cover the investigation of needed blackout symptoms. However, to speed things up, please get in touch with your insurance company to obtain your pre-authorisation code before your appointment.
Self-funding
Our price list is available upon request and displayed in the waiting area of our London Cardiovascular Clinic. Please contact our office for an estimate of the costs.
How to Prevent Blacking Out and Fainting?
To help prevent blacking out and fainting, it’s important to stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Avoid standing for long periods; change positions often and sit down if you feel dizzy. Pay attention to warning signs like lightheadedness—if you experience these, lie down and elevate your legs to improve blood flow.