Breathlessness, also known as dyspnea or shortness of breath, refers to the feeling of discomfort or difficulty in breathing. This sensation can occur after exertion, but when it happens without physical activity, it could be a sign of an underlying condition such as heart failure. Heart failure, or congestive heart failure, is a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, leading to symptoms like breathlessness.
Symptoms of Breathlessness
Breathlessness can vary significantly from person to person and often depends on its underlying cause. However, the general symptoms of breathlessness are:
- Chest pain and tightness
- Difficulty breathing deeply or a feeling of not getting enough air
- Shortness of breath during or after physical activity
- Increased heart rate (palpitations)
Symptoms of Heart Failure
Symptoms of heart failure may vary but generally include:
- Shortness of breath, particularly when walking, lying down, or at rest, and possibly waking up at night gasping for air
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet due to fluid build-up, which may worsen throughout the day
- Persistent fatigue and breathlessness, difficulty with physical activity
- Lightheadedness or fainting
Other less common symptoms of heart failure might include a persistent cough that worsens at night, wheezing, abdominal bloating, loss of appetite, and rapid or irregular heartbeat. Some people may also feel depressed or anxious.
If you experience these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical advice, as they could indicate heart failure or other severe conditions.
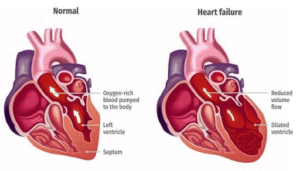
Below is an illustration comparing normal heart to heart failure condition:
Causes of Breathlessness
Symptoms of breathlessness can be influenced by various factors, from temporary conditions to serious health issues. Common causes of breathlessness include:
- Physical deconditioning and obesity: Lack of fitness or excess weight can lead to breathlessness, especially during exertion.
- Heart conditions: Heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmias can impair the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively, causing shortness of breath.
- Lung conditions: Asthma, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), pneumonia, and lung cancer can obstruct or limit airflow, making breathing hard.
- Anaemia: Reduced red blood cells can lead to insufficient oxygen delivery, resulting in breathlessness.
- Anxiety and panic attacks: These can cause feelings of breathlessness and chest tightness.
- Other conditions: Obstructive sleep apnea, high altitudes, and certain medications can also contribute to shortness of breath.
If you experience breathlessness, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to identify and address the underlying cause.
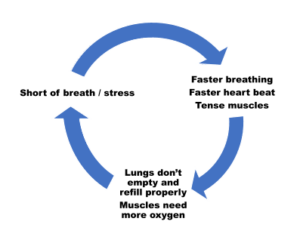
The diagram below shows the connection between breathlessness and anxiety:
Heart Failure Causes
Heart failure can be one of the causes of breathlessness and is triggered by several key conditions that damage or overstrain the heart:
- Coronary Artery Disease: Fatty deposits block blood flow to the heart, potentially causing heart attacks.
- High Blood Pressure: Consistently high blood pressure makes the heart work harder, which can damage it over time.
- Heart Valve Problems: Faulty valves make the heart work harder and can weaken it.
- Cardiomyopathy: Diseases that affect the heart muscle reduce its ability to pump blood effectively.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats force the heart to work harder, which can lead to heart failure.
If you notice symptoms of heart failure like breathlessness, swelling, or extreme tiredness, it’s important to see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage heart failure causes effectively.
Breathlessness Investigation
Your healthcare provider will start with a detailed assessment to determine the causes of breathlessness. This includes discussing your symptoms and potential causes, such as smoking and asthma, conducting a physical exam, and measuring your blood oxygen levels with a sensor.
They may then recommend further tests to pinpoint the issue:
- Imaging Tests: Chest X-ray or CT scans to check for lung or heart issues.
- Blood Tests: To identify conditions like anaemia or other illnesses.
- Lung Function Tests: To evaluate how well your lungs are working.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To assess your heart’s electrical activity.
- Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: To measure how your body handles exercise and oxygen intake.
These tests are often conducted during consultation to develop a management plan and quickly provide peace of mind. They are especially urgent in cases of treatment for shortness of breath due to heart failure.
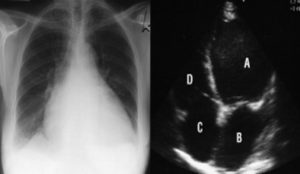
Below is an example of a chest x-ray and echocardiogram of a patient with breathlessness caused by heart failure:
Heart Failure Investigations
To diagnose heart failure, your healthcare provider will start with a thorough evaluation, including discussing your symptoms and medical history and performing a physical exam to look for signs such as swelling and irregular heart sounds.
Key heart failure investigations often recommended include:
- Chest X-ray: To check for heart enlargement and fluid buildup.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To assess the heart’s electrical activity and detect abnormalities.
- Echocardiogram: To create images of the heart and evaluate its pumping function.
- Blood Tests: To identify markers of heart failure and other conditions.
- Cardiac MRI or CT Scan: To provide high-resolution images of the heart.
These heart scans help determine the presence and severity of the condition, guiding your treatment plan.
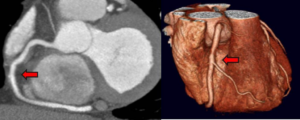
Below is an example of a CT coronary angiogram of the Right Coronary Artery:
Treatment for Shortness of Breath
Treatment for shortness of breath depends on the cause. If it’s heart-related, Dr. Malik will create a personalised treatment plan.
For other causes of breathlessness, your GP will be informed, or you may see a pulmonologist. Treatments can include exercise to strengthen your heart and lungs, relaxation and breathing exercises, medications for asthma or COPD, and oxygen therapy if needed.
While treating the underlying cause often helps, symptoms may return if the condition persists.
Heart Failure Treatment
Treating heart failure involves a comprehensive approach tailored to the severity and underlying causes of the condition. Here’s a summary of the available heart failure treatments:
- Medications: The primary treatment includes diuretics to manage fluid overload and various drugs to enhance heart function and survival. Common heart failure medications in the UK are ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists.
- Devices and Surgery: In advanced stages, additional interventions may be needed. These can include a private pacemaker surgery or a defibrillator (ICD) for abnormal heart rhythms. Surgical options, such as private heart valve surgery or coronary angioplasty procedures, are considered for severe cases.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regardless of the stage, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing other health conditions is crucial.
Each heart failure treatment aims to effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life, focusing on preventing progression.
As a heart failure treatment option, a defibrillator (ICD) is larger than a pacemaker but still goes under the skin:
Ready to Book Your Consultation?
Whether you suspect you experience breathlessness or have a related diagnosis but need expert advice, book your consultation with Dr Malik today. He’ll be more than happy to see you.
Why Choose Dr. Iqbal Malik at London Cardiovascular Clinic?
- Experience: Dr. Malik is a highly experienced cardiologist specialising in diagnosing the causes of breathlessness and heart failure.
- Personalised Care: Every patient gets individual attention with clear advice on managing their condition.
- Advanced Testing: Dr. Malik uses the latest technology to diagnose breathlessness and heart failure symptoms accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Do Breathlessness and Heart Failure Investigations Cost?
Insurance
Most private medical insurance policies cover needed breathlessness investigations. However, to speed things up, please contact your insurance company to obtain your pre-authorisation code before your appointment.
Self-funding
Our price list is available upon request and displayed in the waiting area of our London Cardiovascular Clinic. Please contact our office for an estimate of the costs.
What Are the Risk Factors for Heart Failure?
- Age and Lifestyle: Heart failure risk increases with age, particularly in those over 65. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol use, and a sedentary lifestyle also contribute to this risk.
- Health Conditions: Conditions like coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, heart valve disease, and diabetes raise the likelihood of developing heart failure.
- Previous Cardiac Events: Past heart attacks and irregular heartbeats can weaken the heart muscle and increase the risk.
- Obesity and Sleep Apnea: Obesity and sleep apnea can both lead to heart failure through mechanisms such as increased heart strain and irregular heart rhythms.
- Medications and Infections: Certain medications, including some diabetes drugs and NSAIDs, as well as viral infections, can elevate heart failure risk.
How Can I Lower My Risks of Heart Failure?
You can’t change some risk factors, like age or family history, but you can lower your risk of congestive heart failure by making healthy lifestyle choices. Maintain a healthy weight, eat heart-friendly foods, exercise regularly, manage stress, and avoid tobacco, alcohol, and recreational drugs. It’s also important to take care of any other medical conditions that could increase your risk.
What Are the Types of Heart Failure?
- Systolic Heart Failure: Occurs when the heart muscle is damaged, often due to a heart attack or cardiomyopathy.
- Diastolic Heart Failure: Caused by the heart muscle’s inability to relax properly, leading to reduced efficiency in blood filling and pumping.
- Right-Sided Heart Failure: The right side of the heart struggles to send blood to the lungs, causing fluid to build up in the belly, legs, and feet.
- Left-Sided Heart Failure: The left side of the heart can’t pump blood efficiently, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and causing shortness of breath.
What Are the Complications of Heart Failure?
If you have heart failure, regular checkups are important, even if you feel better. Complications can include kidney damage, changes to heart size or function affecting valves and rhythm, liver damage from fluid buildup, and risks like sudden cardiac death. Other issues may involve irregular heartbeat, heart valve problems, lung fluid, pulmonary hypertension, and malnutrition.
How Can I Prevent Shortness of Breath?
- Avoid Smoke: Stop smoking and stay away from others who smoke to prevent or ease breathing problems.
- Manage Weight: Losing excess weight can help prevent shortness of breath.
- Take It Easy with Tasks: Slow down with activities that strain your breathing.
- Use Sleep Support: Use multiple pillows to prop yourself up while sleeping.
- Follow Prescriptions and Use Inhalers Properly: Take prescribed medications as directed and ensure you use your inhaler device correctly.